Stick around if you're for a complete guide to set up a pyspark environment for data science applications; pyspark functionality as well as the best platforms to be explored.
What is Pyspark?
Pyspark, a robust language that must be considered to learn if you're into the idea of creating more scalable pipelines and analyses. According to Chris Min, a data engineer, Pyspark basically enables writing Spark apps in Python and makes data processing efficient in a distributed fashion. Python is not just a great language, but an all-in-one ecosystem to perform exploratory data analysis, create ETLs for data platforms, and build ML pipelines. You might also say that PySpark is no less than a whole library that can be used for a great deal of large data processing on a single/cluster of machines, Moreover, it has you covered up with handling all those parallel processing without even threading or multiprocessing modules in Python.
Spark is the Real Deal For Data Engineering
According to the International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, the emergence of Spark as a general-purpose cluster computing framework having language-integrated API in Python, Scala, and Java is a real thing right now. Its impressively advanced in-memory programming model and libraries for structured data processing, scalable ML, and Graph analysis increase its functionality in the data science industry. And as matter of fact, it is undeniable that at a certain point of data processing, scaling with Pandas is hard. Being a data engineer involves a lot of large data processing which isn't a big deal if you get well-versed with Spark.
Why Should Data Scientists Learn spark?

https://unsplash.com/photos/AxAPuIRWHGk
Being a data scientist, learning Spark can be a game-changer. For large data processing, Spark is way better than Pandas while not so different in use, so switching to it is not a big deal, and that too when you get real deal benefits while your operations in data engineering. Spark has solutions to various issues and it's a complete collection of libraries to execute logic quite efficiently. Spark ensures you a very clean and efficient experience of operations, even better than Pandas somehow, especially while dealing with large data sets. Spark has you covered up by its efficiently high-performance analysis and user-friendly structure.
Exploring All The Options for Pyspark Setup
I also have a video version of this article, if you are interested feel free to watch this video on my youtube channel
Following is a set of various options you can consider to set up the PySpark ecosystem. The list mentioned below addresses all the best platform that you can consider:
Setting Up Locally Spark and Python On Ubuntu
- Install Java
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
- Download spark from
https://spark.apache.org/downloads.htmllinux version - Set environment variables
sudo nano /etc/environment
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64"
#Save and exit
- To test
echo $JAVA_HOMEand see path to confirm installation - Open bashrc
sudo nano ~/.bashrcand at the end of the file addsource /etc/environment - This should setup your Java environment on ubuntu
- Install spark, after you downloaded spark in step 2 install with the following commands
cd Downloads
sudo tar -zxvf spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz
- Configure environment for spark
sudo nano ~/.bashrcand add the following
export SPARK_HOME=~/Downloads/spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2
export PATH=$PATH:$SPARK_HOME/bin
export PATH=$PATH:~/anaconda3/bin
export PYTHONPATH=$SPARK_HOME/python:$PYTHONPATH
export PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON="jupyter"
export PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON_OPTS="notebook"
export PYSPARK_PYTHON=python3
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin
- Save and exit
- To test
pyspark
Don't have ubuntu?Use VirtualBox
Setup ubuntu on your local using virtualbox. VirtualBox basically enables you to build a virtual computer, and that too, on your own physical computer. You can explore VirtualBox to set up Spark and Python: (20-30 mins approx)
- Start with downloading the Virtualbox.
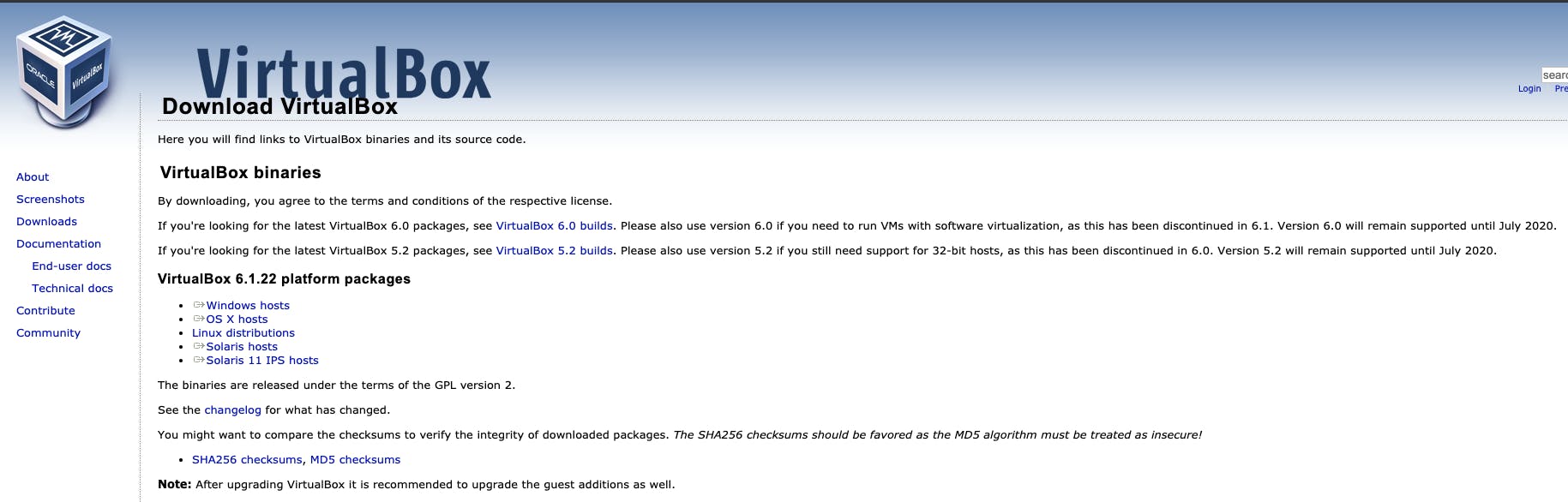
Screenshot from Virtualbox download
- Download ubuntu ISO Image
- In virtual box click on new and setup ubuntu 64 bit environment
- Pass in desired cpu cores,memory and storage
- Point to the downloaded ubuntu image
Setting Up Locally Spark and Python On Mac
- Make sure Homebrew is installed and updated, if not go to this link or type in terminal
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
- Open terminal and Install Java
brew install java
#to check if java installed?
brew info java
- Install scala
brew install scala
- Install Spark
brew install apache-spark
- Install python
brew install python3
- Setup environment bashrc
Open file
sudo nano .bashrc - Add following env variables
#java
export JAVA_HOME=/Library/java/JavaVirtualMachines/adoptopenjdk-8.jdk/contents/Home/
export JRE_HOME=/Library/java/JavaVirtualMachines/openjdk-13.jdk/contents/Home/jre/
#spark
export SPARK_HOME=/usr/local/Cellar/apache-spark/2.4.4/libexec
export PATH=/usr/local/Cellar/apache-spark/2.4.4/bin:$PATH
#pyspark
export PYSPARK_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python3 # or your path to python
export PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON=jupyter
export PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON_OPTS='notebook'
- This should configure the pyspark setup, to test type
pysparkin terminal
Setting up locally with docker and jupyter notebook (My preferred Method)
What is docker?
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Want to learn more about docker, check out this link
Setting up Spark with docker and jupyter notebook is quite a simple task involving a few steps that help build up an optimal environment for PySpark to be run on Jupyter Notebook in no time. Follow the steps mentioned below:
- Install Docker
- Use a pre-existing docker image jupyter/pyspark-notebook by jupyter
- Pull Image
docker pull jupyter/pyspark-notebook
- Docker Run
docker run -d -p 8888:8888 jupyter/pyspark-notebook:latest
- Go to localhost:8888 and create a new notebook, and run cell with
import pyspark
Databricks Setup
Databricks, a unified analytics platform basically has Spark clusters in the cloud that are quite well managed. It is an easy-to-use environment that encourages the users to learn, collaborate and work in a fully integrated workspace. Any spark code can be easily scheduled without any hassle as databricks support pyspark natively
- To start create a databricks account (This is usually done by databricks admins). and link it to your preferred cloud provider. For more information to get started check out this video
- You have to start with creating a Databricks cluster.
- Create a databricks notebook and test by
import pyspark
Spark and Python on AWS EC2
Amazon EC2, are virtual machines provided by AWS, these come with pre-installed os software AMIs but the rest of the dependencies would need to be installed separately.
- Go to AWS Console and EC2
- Select Ubuntu AMI
- Follow the steps from Option 1
Avoid doing this and use other options
Pyspark on AWS Sagemaker Notebooks
Launched in 2017, Amazon SageMaker is a cloud-based machine-learning platform that is fully managed and decouples your environments across developing, training, and deploying, letting you scale them separately whilst helping you optimize your spending and time. It is really easy to spin Sagemaker notebooks with a click of a few buttons. Amazon SageMaker notebook instance is a machine learning (ML) compute instance running the Jupyter Notebook Environment. It comes with pre-configured Conda environments like python2, python3, PyTorch, TensorFlow etc
- Log in to your aws console and go to Sagemaker
- Click on Notebook, Notebook Instances on the left side
- Click on Create Notebook Instances, give it a name and select desired configurations
- Select instance type, maybe start small ml.t2.medium, and maybe you can spin up a powerful instance later
- Click create and wait for a few minutes and then click on open jupyterlab to go to the notebook
- Create a new notebook and write the following code snippet to run pyspark
import sagemaker_pyspark
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, DataFrame
classpath = ":".join(sagemaker_pyspark.classpath_jars())
spark = SparkSession.builder.config(
"spark.driver.extraClassPath", classpath
).getOrCreate()
- If you are interested to know more about Sagemaker, do check out my previous video, Sagemaker in 11 Minutes
AWS EMR Cluster Setup
Amazon EMR, probably one of the best places to run Spark, can help you create Spark clusters very easily as it is equipped with various features such as Amazon S3 connectivity which makes it all lightning-fast and super-convenient. Moreover, integrated operations with EC2 spot market and EMR Managed scaling.
To be precise, EMR is a well-managed big data service enabling data scientists to get assistance in their work with data science applications written in Python, Scala, and Pyspark. It ensures a convenient cluster setup for Spark for the data scientist to have a platform to develop and visualize.
- Go to AWS console and search for EMR
- Click on create a cluster
- In general configuration give it a name, in Software configuration select Spark Application
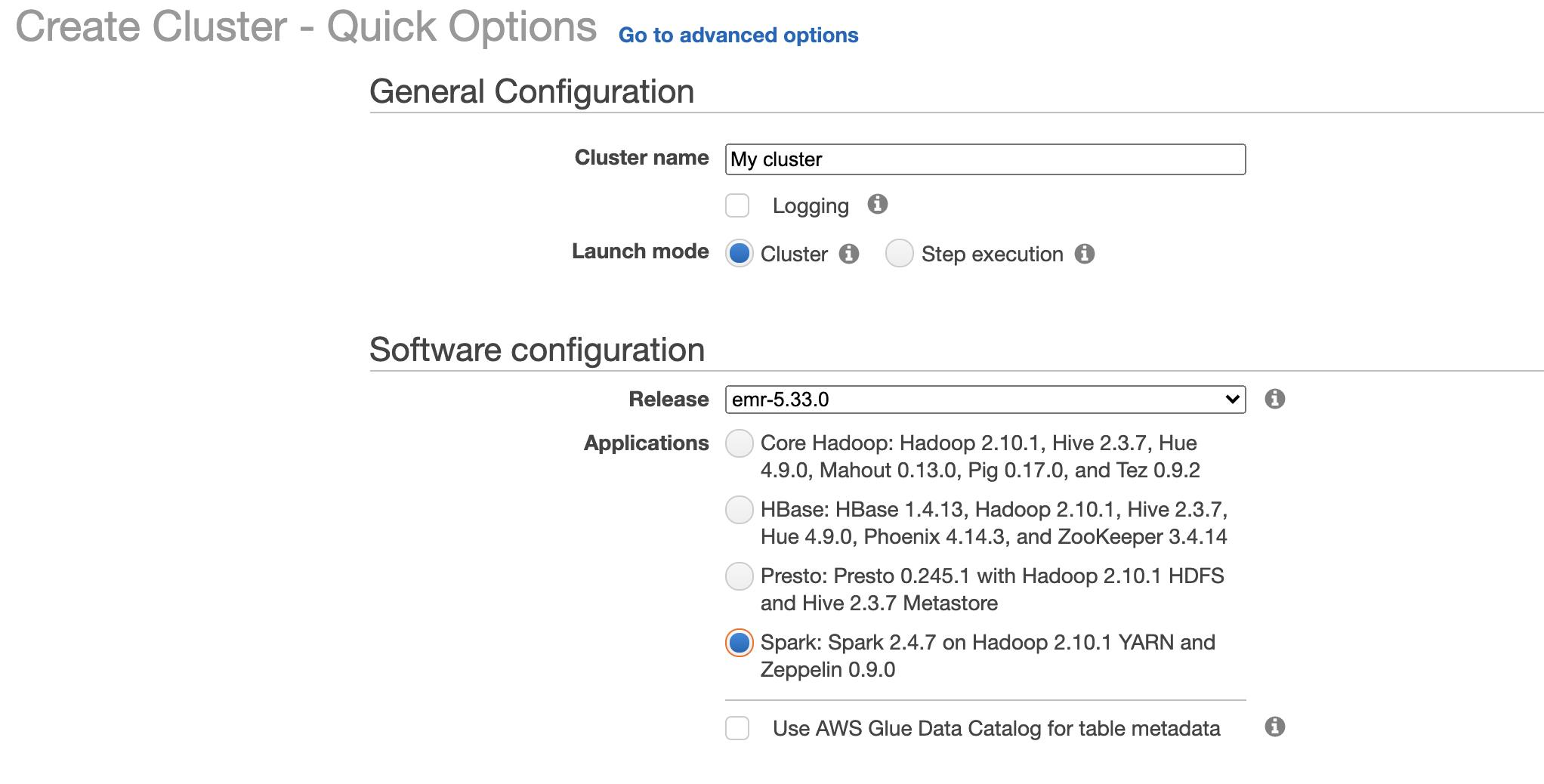
- In Hardware configuration select instance type, maybe start small from m1.medium and select number of instances in cluster
- In Security Select EC2 Key pairs, usually created by administrator, if not you can follow the steps on the right to create programmatic access keys for the cluster to use
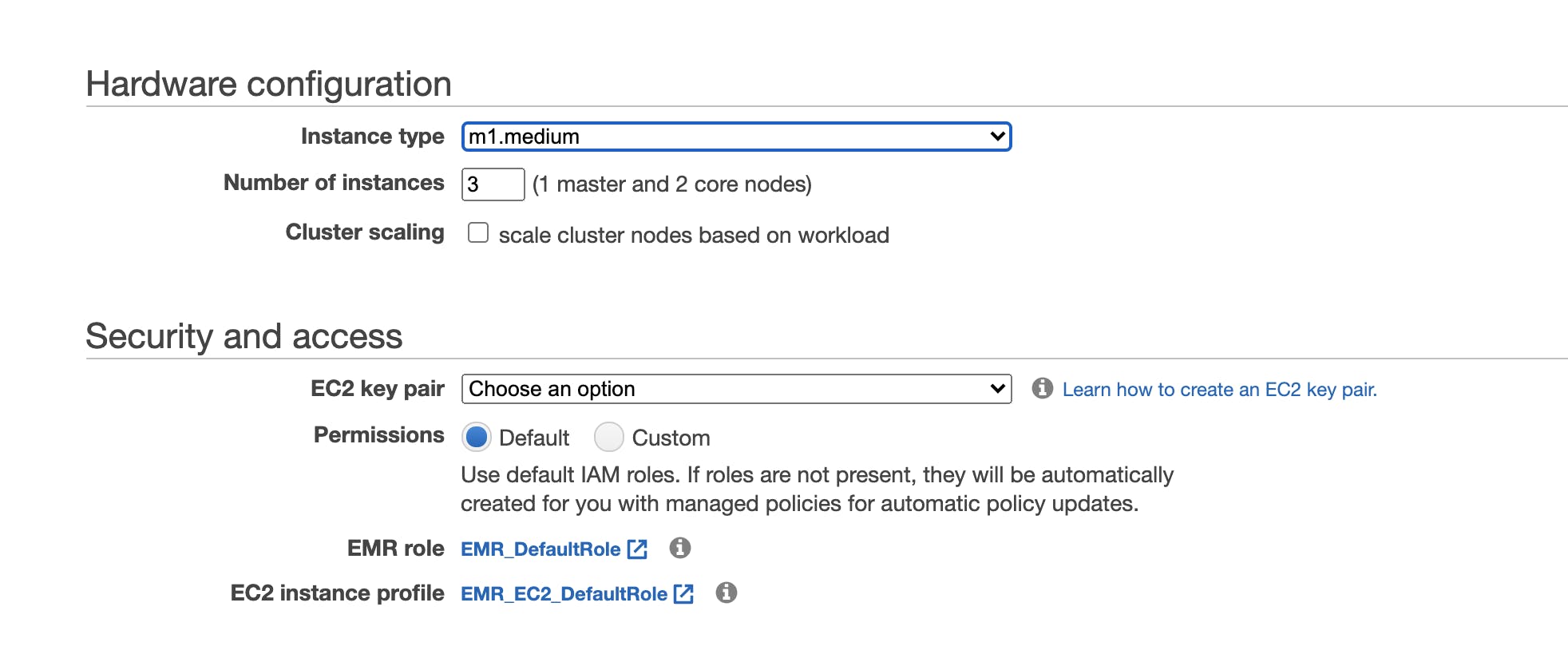
- Keep the rest options to default and create the cluster
- After that create a EMR notebook and select the newly created cluster to execute your jobs for scale
Conclusion:
Spark, a complete analytic engine, helps data scientists in their operations of lengthy data processings that are rather difficult when handled with Pandas. Thus, learning PySpark, the robust library, can help data engineers a lot in their course of work. Now that you know various platforms that enable you setup Spark clusters with well managed clouds, you can explore them yourself.
